Abstract
Background. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems have the potential to revolutionize the fields of medicine and dentistry by identifying solutions for managing multiple clinical problems. This greatly facilitates the tasks of physicians. Bibliometric studies not only provide insight into the history of a particular topic, but also help to determine how the work evolves over time, and to identify interesting new research.
Objectives. The aim of the present study was to identify and analyze bibliographically recent research articles on the use of AI in endodontics.
Material and methods. The search was conducted in March 2024 in the Web of Science Core Collection (WoS-CC), using the Clarivate™ search engine. The search strategy in all fields included in the database was as follows: “endodontics” was the main keyword, and the other keywords were “artificial intelligence”, “deep learning”, “machine learning”, “artificial neural network”, and “convolutional neural network”. The title, authors, institution, country, impact factor, total number of citations, year of publication, journal name, number of authors, keywords, abstracts, and other topics of interest were recorded. Bibliometric networks were generated and analyzed using the Visualization of Similarities Viewer (VOSviewer).
Results. Of the 54 articles published by the journals indexed in the WoS-CC between 2012 and 2024 that contained the search terms, 40 were included in this study. The article citations ranged from 0 to168, with an average of 18.97. The number of countries contributing to the research was 29. The country with the highest contribution rate in the field was the USA ranked first (27.5 %), followed by Germany (17.5 %), China (15.0%), and India (15.0%).
Conclusions. Based on this review, it can be concluded that a more significant research interest in AI and endodontics was observed in the USA. The most cited research articles dealt with dental image diagnosis with the use of convolutional neural networks (CNN), the radiologic diagnosis of apical lesions using AI, and the computer-aided diagnosis of periapical lesions using AI in computed tomography (CT) analyses.
Keywords: artificial intelligence, endodontics, citation analysis, bibliometrics
Introduction
Planning a research idea, obtaining study data by successfully applying an appropriate method, and analyzing and comparing the data with other studies in the literature are the stages that must be carefully managed in preparing a scientific publication.1 Research is deemed worthy of publication in a scientific journal if it will attract the attention of researchers, be frequently cited and make a scientifically meaningful contribution to the field under investigation.2 Bibliometrics assesses academic productivity using quantitative measures, with the aim of analyzing and monitoring the development and structure of science.3 Bibliometric studies enable the evaluation of the contribution of particular countries to the scientific literature in certain disciplines and topics, as well as the assessment of journals through comparative studies.4 The number of citations an article receives may not reflect its scientific quality or impact on clinical practice, but it is considered an objective indicator for researchers to track new trends and make evidence-based decisions with regard to technological development in the field.5, 6
The rationale underlying bibliometric research is that analyzing articles on a specific topic in peer-reviewed journals can provide clinicians and researchers with a historical perspective on the progress of the topic. It can also help to identify where research is most concentrated and how areas of interest have changed over time.3 The first bibliometric analysis in endodontics addressed trends in endodontic research by examining the top 100 most cited articles.7
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a field of applied computer science, first defined by John McCarthy. The development of AI is often referred to as the “fourth industrial revolution” due to its ability to simulate critical thinking, intelligent behavior and human-like decision making based on computer technology.8, 9 Recent interest in AI is due to the development of a new generation of specialized algorithms capable of analyzing and predicting, using large datasets.10
Artificial intelligence has found its application in areas of medicine and dentistry, as well as in all kinds of industries.11, 12 Artificial intelligence systems have the potential to revolutionize the fields of medicine and dentistry by identifying solutions for managing multiple clinical problems. This greatly facilitates the tasks of physicians.8 Today, modern medicine is witnessing a revolution with the application of AI in clinical decision making. Artificial intelligence has been shown to improve efficiency and accuracy in a timely manner at a lower cost, with results comparable to those reached by medical professionals.13 However, the implementation of AI systems is becoming increasingly complex due to emerging potential risks and ethical challenges that must be considered from a legal standpoint.14
The application of AI has not become routine in dental clinical practice.15 However, pathology detection,16 caries diagnosis,17 robotic assistance,18 and electronic record retrieval19 with the use of AI have been gaining acceptance in dentistry.
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of papers reporting the application of AI models in endodontics. The determination of root canal working length,20 the detection of vertical root fractures,21, 22 the success of root canal treatment,23 the detection of pulp diseases,24 the detection and diagnosis of periapical lesions,25 the detection of unfilled canals,26 the prediction of postoperative pain27 and case difficulty28 are the main focus in some of the studies conducted in this field.
Artificial intelligence research in endodontics has grown alongside other dental specialities.8 In recent years, bibliometric research has been conducted in many fields of dentistry.7, 29, 30 As far as we are aware, no bibliometric analysis of AI studies in the field of endodontics has been published. From this perspective, the aim of the present study was to bibliometrically evaluate studies using AI models in the field of endodontics.
Material and methods
A systematic search of the literature was conducted using the Web of Science Core Collection (WoS-CC) online database and the Clarivate™ search engine to identify relevant research in the field. An electronic search was conducted on March 2024. The search strategy for all fields included in the database applied the main keyword “endodontics” and other keywords: “artificial intelligence”; “deep learning”; “machine learning”; “artificial neural network”; and “convolutional neural network” [((artificial intelligence) OR (deep learning) OR (machine learning) OR (artificial neural network) OR (convolutional neural network)) AND (endodontics)]. A total of 54 studies published between 2012 and March 2024 were identified in the scanning. Articles that were not directly related to the subject, or were related only to disciplines other than endodontics, were excluded. After a thorough review of all articles, 2 investigators excluded 6 proceeding papers, 1 editorial material and 7 irrelevant articles. Thus, a total of 40 articles were included in the study. They were then ranked according to the frequency of citations and were further analyzed.
Each article was thoroughly reviewed, and basic information, including the study design, was recorded. The data was imported into the application using a tab-delimited file tool; this data included the full record and the cited references. The following information was recorded: title; authors; institution; country; impact factor; total number of citations; year of publication; journal name; number of authors; keywords; abstracts; and other topics. The Visualization of Similarities Viewer (VOS Viewer) software, v. 1.6.19 (Centre for Science and Technology Studies, Leiden University, the Netherlands), was used. An algorithm for automatic term data identification was used to map the bibliometric network of the exported data.31
With regard to the aim of the present study, the questions to be answered are listed below:
1. What is the distribution of articles written on the topic by years?
2. Which countries are the highest contributors?
3. Which journals publish the highest number of articles in the field?
4. Who are the most cited authors and what are the most cited publications?
5. What is the most common use of AI in endodontics?
Results
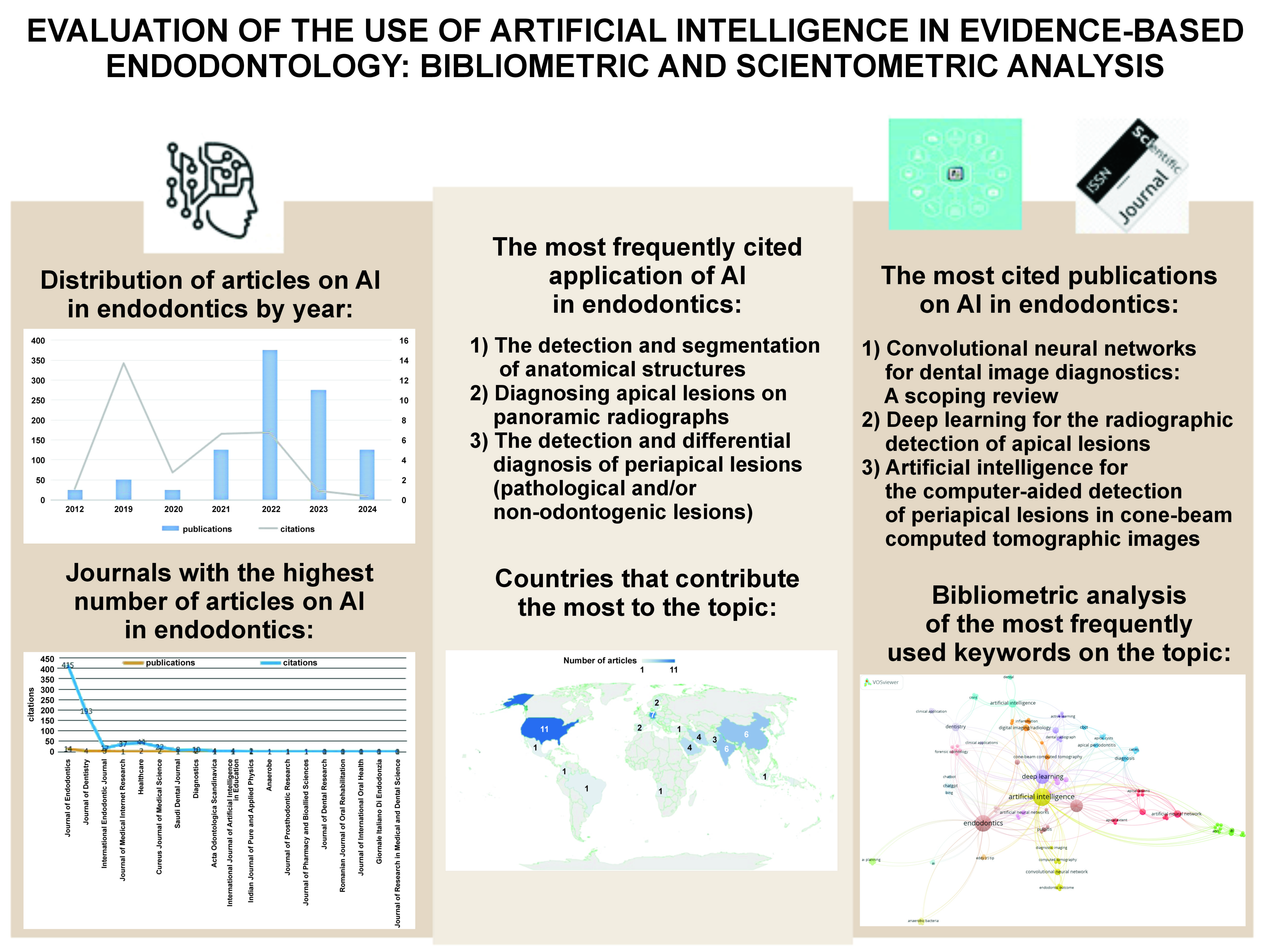
A total of 40 articles were included in the study; they were all published in indexed journals (WoS-CC, the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE)) between 2012 and 2024. The distribution of the number of publications and citations over the years is shown in Fig. 1.
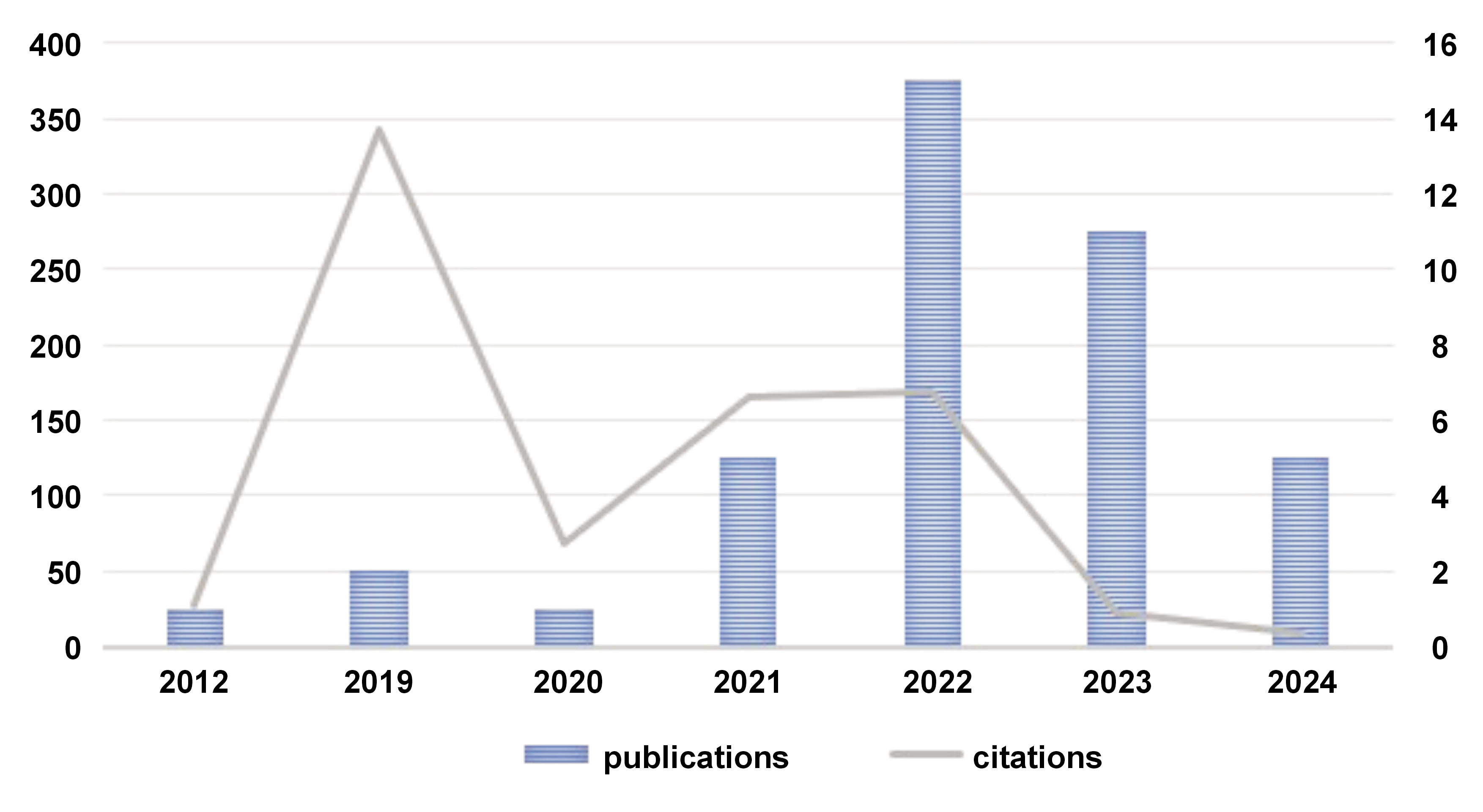
The countries of all authors (not only first authors) who contributed to the articles are shown in Fig. 2. The highest contribution came from the USA, with 11 articles. The countries of origin of the authors who published the most articles on the topic were the USA (11) ranked first, followed by Germany (7), China (6), and India (6). Other countries with the number of articles published are as follows: Saudi Arabia (4); Iran (4); South Korea (3); Denmark (2); Pakistan (2); and Spain (2); and the UAE, Angola, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Czech Republic, Colombia, England, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, the Netherlands, Romania, Slovakia, Sweden, Thailand, Turkey, and Wales (1). Although a total of 40 articles were included in the study, the number of contributing countries exceeded the number of articles, since some publications had international co-authorship from multiple countries.
A total number of 103 contributing institutions was determined based on the authors’ addresses. The analysis of the country of origin using VOSviewer showed that 29 countries contributed to research and publications in the field, both with and without collaboration.
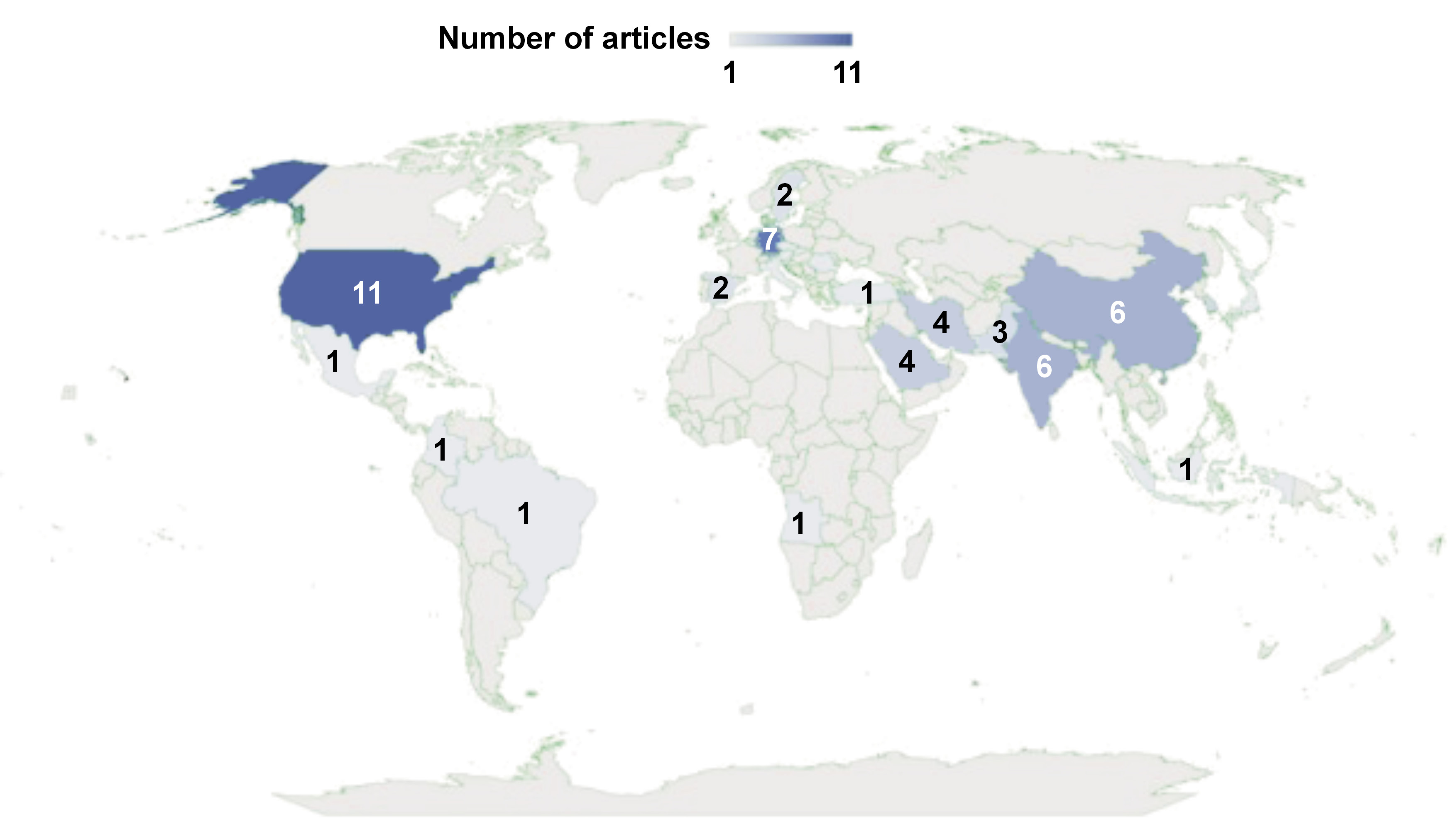
The citation analysis of articles was conducted by selecting countries that had published at least one article and received at least one citation, and 24 countries were observed to have the most connections (Fig. 3). While the countries of origin of the most cited articles were Germany and the USA, the countries of origin of the authors who published the most articles on the topic were the USA, Germany, China, and India. In terms of the total link strength of the countries of origin of the articles on the topic, the USA ranked first, Germany ranked second, followed by China and India. The article citations ranged from 0 to 168, with an average of 18.97. Two articles received over 100 citations.
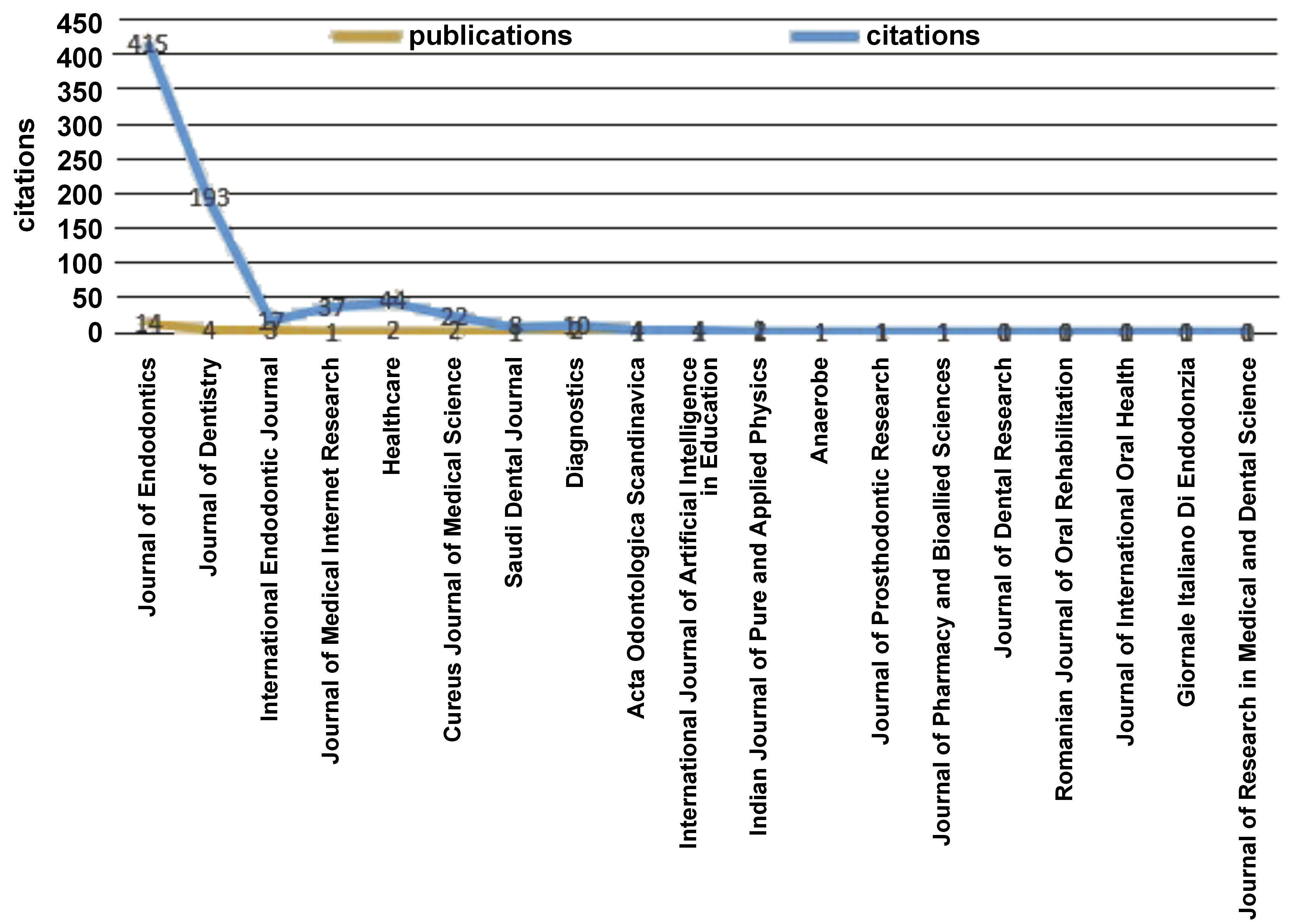
The comparison of the total number of citations of the journals related to the subject and the number of publications is shown in Fig. 4. The Journal of Endodontics has published the highest number of articles – 14 articles (35%). The Journal of Dentistry with 4 articles (10%) followed the Journal of Endodontics. The International Endodontic Journal took the 3rd place with 3 articles (7.5%).
When examining the first authors of the 3 most cited publications, Schwendicke is ranked first, followed by Ekert in the 2nd place and Setzer in the 3rd place. It was found that 217 authors were involved in articles on the topic of AI in endodontics. Schwendicke was the most cited author with a total of 335 citations in 3 articles. Krois and Golla followed, with a total number of 317 citations, each with 2 articles (Table 1).
Based on the scientometric evaluation, the AI application that received the most focus in endodontics was the detection and segmentation of anatomical structures using AI on dental radiographs, and the diagnosis of periapical lesions in radiographic and tomographic images, followed by the analysis of canal morphology (C-shaped canals and second mesial buccal (MB2) canals).
The 10 most commonly used keywords and their frequency of occurrence in the included articles, as well as their total link strength, are shown in Table 2. The most cited article was published in the Journal of Dentistry in 2019, the 2nd most cited article was published in the Journal of Endodontics in 2019 and the 3rd most cited article was published in the Journal of Endodontics in 2020. The list of publications is presented in Table 1 in order from the most cited to the least cited.
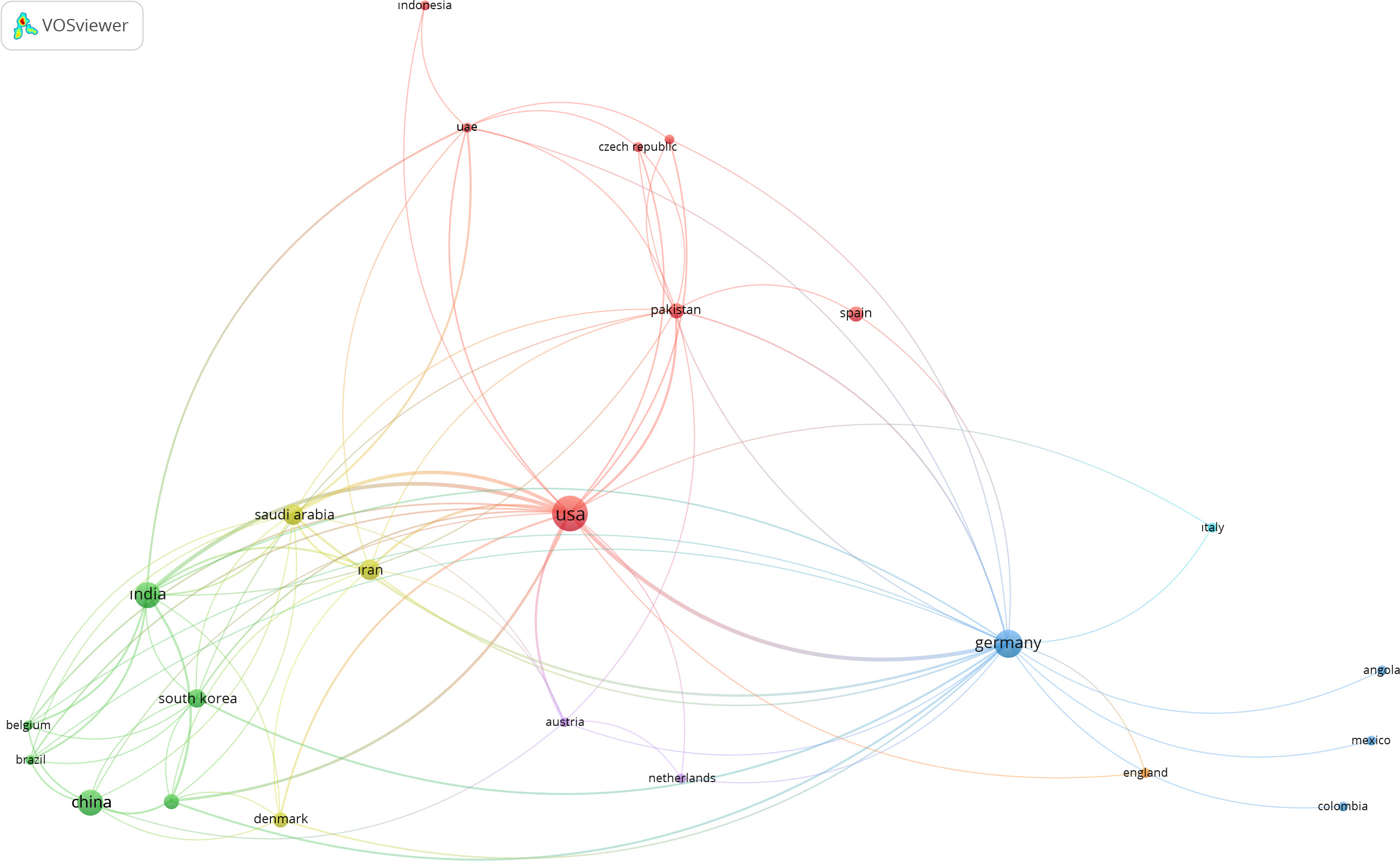
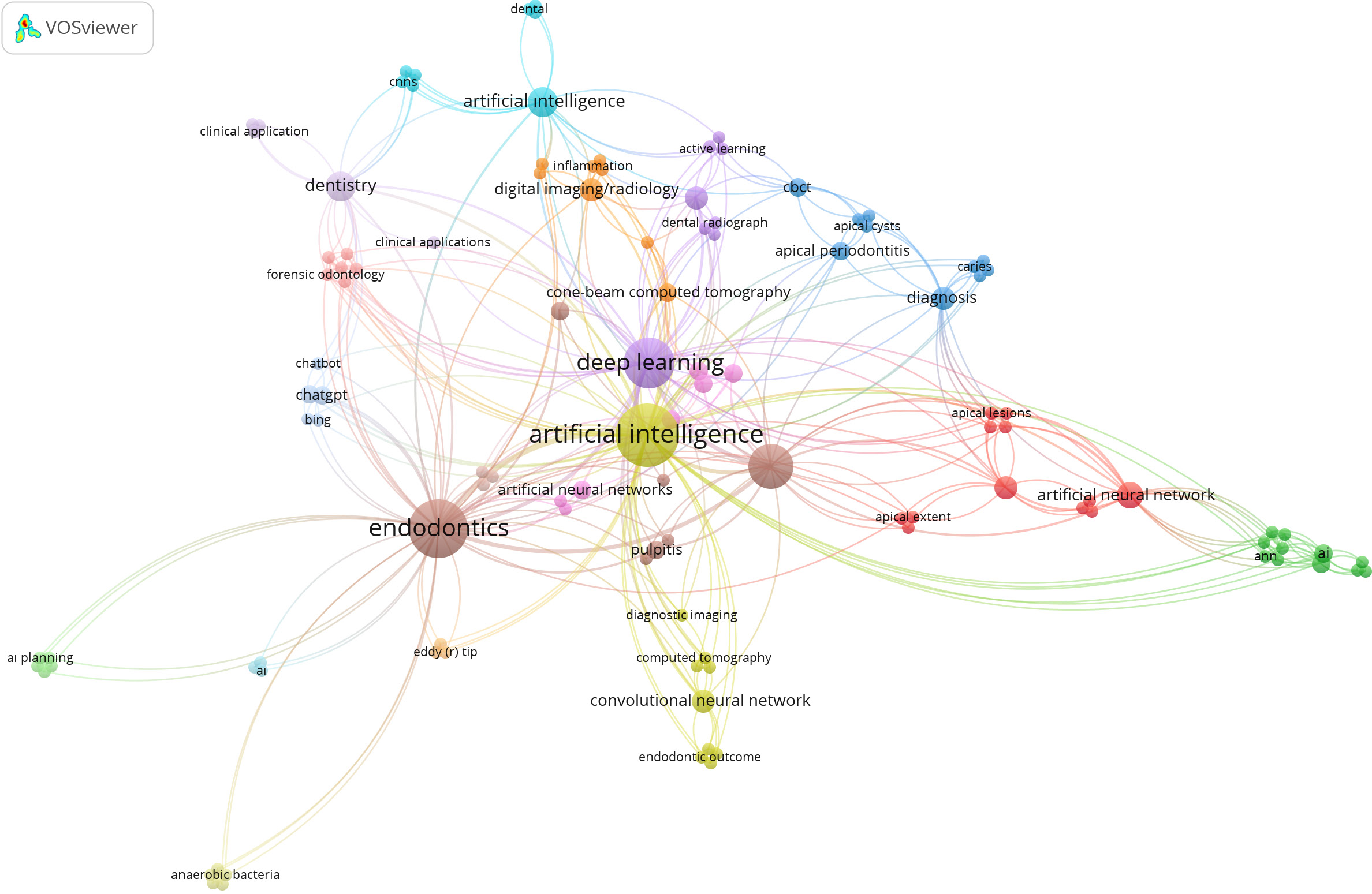
When a bibliometric analysis was performed according to keyword, it was observed that the most frequently used words in studies on AI in endodontics were “artificial intelligence”, “endodontics” and “deep learning”, followed by “machine learning”. In total, 124 unique keywords were identified in the included studies. In Fig. 5, the size of a node represents the frequency of use of the word in the published articles.
Discussion
Bibliometric studies not only provide insight into the history of a particular topic, but also help to determine how the work evolves over time, and to identify interesting new research.32 Bibliometric studies can evaluate the most cited publications of a journal.33 Moreover, they can focus on the scientific production of a particular country or field of research.34 Given this background, the aim of our study was to provide a bibliometric evaluation of research on AI in endodontics. This is a current concept in endodontics and dentistry.
The WoS-CC database was searched following the methodology used in another recent endodontic bibliometric review.35 The WoS-CC is a popular and suitable database for bibliometric analysis, as it has a large database of publications dating back to 1945.36 However, other similar scientometric or bibliometric studies in the field have used other databases, such as Scopus or MEDLINE/PubMed®, to obtain data.34, 37 After comparing the available evidence in this area, it was decided to conduct an individual search in a single database (WoS-CC) for the current study. Although the use of more than one database for search may have made more studies available, at this stage, there could have been duplicate publications needing to be removed manually. The presence of duplicate records would alter all the quantitative bibliometric parameters, potentially leading to the misinterpretation of the relationships between different research components. Thus, only one database was included.
Although it has been claimed that bibliometric analysis should be carried out on topics that have been studied for many years, it is confirmed that the articles published and cited in journals tend to be current topics.33, 38 Artificial intelligence in endodontics is a hot topic. Therefore, in this study, the authors do not consider the fact that the research was conducted on a current issue as a limitation.
The combined data analysis with the use of the bibliometric and network tools of WoS-CC provided many results referring to endodontics and AI. Publications on AI in endodontics continued to increase from 2021 to 2022, peaking in 2022, and decreasing slightly in 2023. This could be an indication that AI is becoming more popular as technology advances, while the topic is becoming more interesting and worthy of discussion through research publication.
The analysis of country of origin and the research institution was conducted using VOSviewer; it showed that 29 countries contributed to research and publications in this field, either collaboratively or non-collaboratively. The country that contributed the most in the field of AI and endodontics was the USA, which can be attributed to the fact that this country has experienced an increase in the number of researchers and working groups in the field of endodontics, and it has followed the technological development.
It is also important to identify the most influential journals for the publication and dissemination of AI and endodontics research. This can help researchers to follow specific journals and aim to publish their research in sources that show specificity in a scientific field.37 Comparing the number of articles n AI published in scientific journals, the Journal of Endodontics had the highest number of publications in the categories of “Dentistry” and “Endodontics”, with 14 articles. As a result of the analysis, the Journal of Endodontics was also found to be the journal with the highest total number of citations of articles related to AI in the field of endodontics. One of the reasons for this may be that this journal has published the highest number of articles on the topic and that the journal closely follows current topics in the field of endodontics, and finds them worthy of publication. Additionally, as the journal is in the Q1 quartile of the “Dentistry, Medicine and Oral Surgery” category, its citation rate is high and very popular. The fact that the journal follows all advances in endodontics and that it is indexed in SCIE may be attractive factors for researchers when choosing a journal. The Journal of Dentistry followed the Journal of Endodontics, with 4 articles. The journal International Endodontic Journal took the 3rd place, with 3 articles. An important observation about journals is that, although AI is mostly about diagnostics and radiology, diagnostic and radiological reviews in endodontics are more likely to be published in endodontic journals rather than in general dentistry or radiology journals.
The most cited articles on AI in endodontics play a crucial role in the field. Their knowledge draws public attention to researchers who have influenced the growth and development of the work.7 According to the analysis conducted in our study, Schwendicke was the most cited author on the topic. In a 2019 review, Schwendicke et al. reported studies on the detection and segmentation of anatomical structures in different areas of dentistry using AI on dental radiographs.39 The 2nd most cited article was that of Ekert et al., who detected apical lesions on radiographs using AI, and found that AI gave satisfactory results in diagnosing apical lesions on panoramic radiographs.40 In the 3rd most cited article, Setzer et al. used AI to detect apical lesions on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images and reported that, in the long term, the addition of automated image analysis based on three-dimensional (3D) imaging could assist clinicians in lesion detection and the differential diagnosis of periapical lesions (pathological and/or non-odontogenic lesions) in combination with previous examinations.41 In this context, it can be concluded that the most cited articles have paved the way for dental diagnosis, the detection of dental pathology, and even differential diagnosis using AI in endodontics. Dental diagnosis using AI may also help to reduce the time spent by clinicians on making a diagnosis.
Although the most cited article on AI is a review article analyzing general dentistry fields, including endodontics, the 2nd and 3rd most cited articles are about the use of AI in the diagnosis of apical lesions in panoramic radiography and on CBCT images, published in a journal in the field of endodontics. We can say that the number of citations of publications on AI in the field of endodontics competes with publications on the use of AI in dentistry.
The keyword co-occurrence analysis can be an insight into the development patterns of a particular area of scientific research.35 As shown in Table 2, the first 10 keywords were often repeated, and the most often repeated keyword among them was “artificial intelligence”. This was followed by the keywords “endodontics” and “deep learning”. However, it was also observed that keywords such as “machine learning”, “artificial neural network” and “convolutional neural network” were used as well. Artificial intelligence is a general term that comprises more specific topics, including deep learning, machine learning and artificial neural networks. The results of our keyword analysis show that studies using the concept of AI have begun to specialize in the branches of AI, leaving the general concept behind over time.
One limitation could be a small number of articles included in our study. This was due to the fact that the concept of AI is a current topic, and studies using AI have recently been undertaken in the field of endodontics, as in almost all fields.
Conclusions
The use of AI in dental research has steadily increased since the first applications were reported in 2012, but the “explosion” of research occurred in 2019.39 Indeed, the number of papers reporting on AI models applied in endodontics has raised significantly in recent years. The determination of root canal working length,20 the detection of vertical root fractures,21, 22 the success of root canal treatment,23 the detection of pulp diseases,24 the detection and diagnosis of periapical lesions,25 the detection of unfilled canals,26 the prediction of postoperative pain27 and case difficulty28 are some of the issues covered by the studies conducted in this field. In the years that followed, the use of AI in endodontics expanded. Studies were conducted on its use in preclinical education.42 To date, AI in endodontics has had many applications, which we have analyzed bibliometrically. For example, the use of a conventional neural network to detect apical lesions based on panoramic radiographs can help dentists in their diagnostic efforts. However, for such approaches to be widely used in clinical settings, their sensitivity needs to be improved via further studies.
The present bibliometric analysis reviewed current trends, as well as leading countries and journals in terms of research focusing on the use of AI applications in endodontics. Our study considered publications related to AI in endodontics to highlight the bibliometric characteristics of a specific topic. Further research could focus on AI in endodontics in a broader context.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Data availability
The datasets supporting the findings of the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Use of AI and AI-assisted technologies
Not applicable.